How Unified Threat Management Redefines Network Security
Introduction
Today’s organizations face unprecedented cyber risks, with threats evolving in sophistication and frequency. This complexity makes it challenging for security teams to defend against malware, phishing, ransomware, and unauthorized intrusions while maintaining operational agility. To address this, businesses are increasingly considering unified threat management (UTM) systems. By consolidating multiple security functions—including firewalls, intrusion prevention, and antivirus—into a single integrated solution, UTM brings comprehensive protection and streamlined management to modern network security.
Implementing a unified approach simplifies network security architecture, enhances operational efficiency, and provides greater visibility across the entire organization’s security posture. This integrated model empowers IT teams to identify and react to threats faster while ensuring compliance with evolving regulations and reducing the costs associated with running multiple standalone systems.
What Is Unified Threat Management?
Unified Threat Management (UTM) is an all-in-one security solution that combines a wide array of essential security tools and processes within a single management console. Designed to reduce cost and complexity, UTM systems provide a cohesive barrier against threats like viruses, malware, data breaches, and hacking attempts. Centralized control and real-time analytics simplify monitoring and mitigating diverse security risks. TechTarget’s explanation of UTM fundamentals and core capabilities is a useful resource for further details on UTM fundamentals and core capabilities.
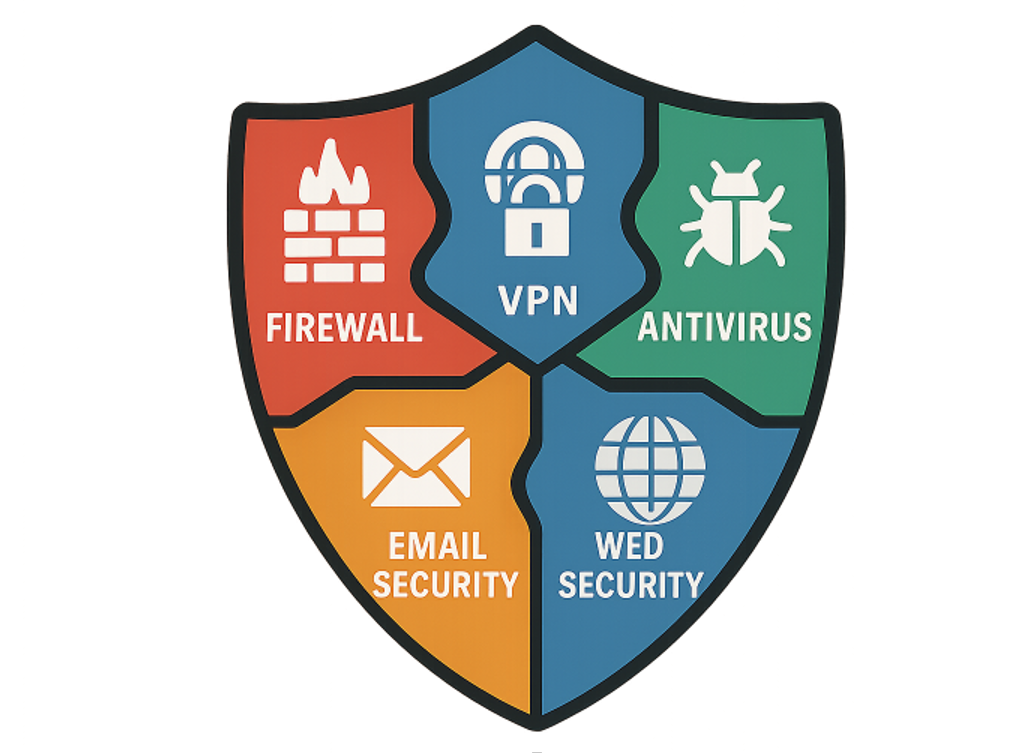
Core Components of UTM Systems
The architecture of typical UTM solutions can be broken down into several core components:
- Firewall and Intrusion Prevention: Monitor network traffic and block unauthorized access attempts or potentially malicious packets.
- Virtual Private Network (VPN): Secure tunneling for remote access and securing connections between multiple sites.
- Web Security: URL filtering, antivirus, and protection against malicious websites help prevent drive-by downloads and phishing attacks.
- Email Security: Anti-spam, anti-phishing, and mail antivirus capabilities block threats and filter unsolicited messages.
- Antivirus and Anti-malware: Continuous scanning for known and unknown malicious files helps to detect threats at the network gateway.
When combined, these modules form a robust, centralized security posture, making it significantly easier to manage and enforce organization-wide policies.
Benefits of Implementing UTM
Centralized Security Management
UTM’s single-pane-of-glass approach allows security teams to administer rules, generate reports, and respond to incidents from one dashboard. This saves critical time during security events, enhancing the organization’s ability to react to and contain breaches quickly.
Operational and Cost Efficiency
With a unified platform, organizations eliminate the need for multiple vendor contracts, licensing schemes, and hardware footprints. Maintenance, updates, and upgrades are streamlined, freeing up valuable IT resources and reducing costs over the lifespan of the security infrastructure. This efficiency extends to compliance, where UTM systems simplify meeting regulatory standards through centralized reporting and built-in compliance features.
Consistent Security Enforcement
UTM systems ensure that all network segments are subject to the same security protocols—critical for geographically distributed organizations or those with hybrid network architectures. According to CSO Online, this consistency is vital for enforcing company-wide standards and minimizing potential gaps that attackers could exploit.
Challenges and Considerations
Scalability Limitations
UTM appliances are generally designed for ease of use and swift deployment, but some may encounter limitations as the organization grows. High-traffic environments can push the hardware’s resources to their limits, causing reduced efficiency or, in extreme cases, outages. Cloud-native security solutions tend to scale more flexibly, so it’s vital to assess future growth when considering UTM deployment.
Performance and Complexity
Consolidating multiple intensive security tasks onto a single device can cause processing bottlenecks, especially during peak demand or sustained attacks. It is crucial to choose a UTM solution with the capacity and redundancy to match current and projected workloads.
See also: How Technology Has Changed the Music Industry
UTM in the Context of Modern Network Security
The shift toward integrated security and networking—commonly termed “secure networking”—reflects the need for consolidated, responsive defense solutions. Industry innovators are now integrating unified management and analytics, providing CIOs with enhanced visibility and real-time enforcement across cloud, data center, and hybrid deployments. Modern security design prioritizes deep intelligence and adaptive controls to handle evolving threats and increasingly distributed workforces. As explored in a recent CNBC report, the drive for more advanced cybersecurity is powering rapid investment and technological advancement in this arena.
Real-World Applications of UTM
UTM solutions are widely used in organizations of all sizes, from small businesses to multinational enterprises and public sector entities. For example, healthcare providers employ UTM to secure sensitive patient records and maintain regulatory compliance, while educational institutions use them to filter web content and defend against malware outbreaks. In the era of artificial intelligence, industry leaders like Cisco are integrating security more deeply into network fabric, allowing companies to pursue zero-trust architectures and accelerate secure digital transformation for AI-powered operations. This approach empowers enterprises to match the pace of threat actors leveraging AI for more frequent and sophisticated attacks.
Future Trends in UTM
The increasing reliance on AI and automation for proactive threat detection and incident response is shaping the future of unified threat management. As remote work and hybrid cloud adoption become the norm, UTM platforms will likely evolve to offer more flexible, cloud-native deployments and improved user experience for remote employees. Integration with security orchestration and automation response (SOAR) tools, expanded threat intelligence feeds, and the ability to adapt dynamically to zero-trust architectures are key trends to watch in the next generation of UTM solutions.
Conclusion
Unified threat management (UTM) stands out as a pivotal element in an organization’s security framework, marrying diverse protective measures into a unified, centrally managed platform. While scalability and performance issues require careful consideration, the operational simplicity and robust defense UTM provides make it a powerful choice for businesses aiming to build resilient, forward-looking cybersecurity strategies.